“Struggling with overeating”
“Always resorting to quick, easy meals due to lack of time”
“Frequent dining out”
It’s not uncommon for individuals leading busy lives to find it challenging to maintain a balanced diet and ensure proper nutrition. However, it’s crucial to be aware that consistently overeating or having a nutritionally unbalanced diet can lead to persistently high blood sugar levels. This not only increases the risk of obesity but also elevates the likelihood of developing health conditions such as metabolic syndrome and diabetes.
While it’s essential to incorporate physical activity and rectify irregular lifestyle habits to combat metabolic syndrome and diabetes, the first step should be to modify your dietary habits. Our bodies are essentially built from what we consume daily. Therefore, by accurately identifying and integrating the nutrients you require, you can optimize your body’s health and functionality.
There’s a plethora of food items deemed beneficial for our health, but one that stands out for its effectiveness in controlling blood sugar levels is the Jerusalem artichoke. The dietary fiber known as “inulin,” found in Jerusalem artichokes, has been reported to help curb the rise in blood sugar levels after meals. Hence, Jerusalem artichokes are often referred to as “natural insulin,” making them a key ingredient that individuals with diabetes, metabolic syndrome, or those at risk should consider incorporating into their diet.
This article provides insights into the advantages of including Jerusalem artichokes in your diet, suggests effective ways to consume them, and discusses the desirable changes in blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes and metabolic syndrome. We hope you find this information useful and encourage you to use it as a guide to healthier eating habits.
The Key to Alleviating Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Lies in Gradual Blood Sugar Regulation
In order to mitigate conditions such as metabolic syndrome and diabetes, it’s crucial to ensure a gentle rise in blood sugar levels, striving to keep them as close to normal values as possible.
Typically, the intake of carbohydrates through meals leads to a gradual increase in blood sugar levels. Insulin then brings these levels back to a fasting state approximately two hours later.
However, if the secretion of insulin is inadequate or if it fails to function effectively, there can be instances where post-meal blood sugar levels remain elevated or experience drastic fluctuations, known as blood sugar spikes. Such scenarios can potentially result not only in obesity but also in serious health conditions like diabetes and stroke, thereby placing a significant burden on the body.
In this section, we aim to highlight the importance of blood sugar control. We do this by explaining the changes in post-meal blood sugar levels across three distinct categories: “healthy individuals, pre-diabetic individuals, and individuals with diabetes.”
Post-Meal Blood Sugar Level Changes at 1 Hour/2 Hours/3 Hours
The importance of blood sugar control becomes evident when we consider the following three patterns of post-meal blood sugar changes:
Healthy individuals: Those with normal blood sugar levels
Pre-diabetic individuals: Those whose blood sugar levels remain elevated even two hours after a meal
Individuals with diabetes: Those who consistently experience high blood sugar levels
We invite you to examine the compiled graph that illustrates the changes in post-meal blood sugar levels across these three categories.
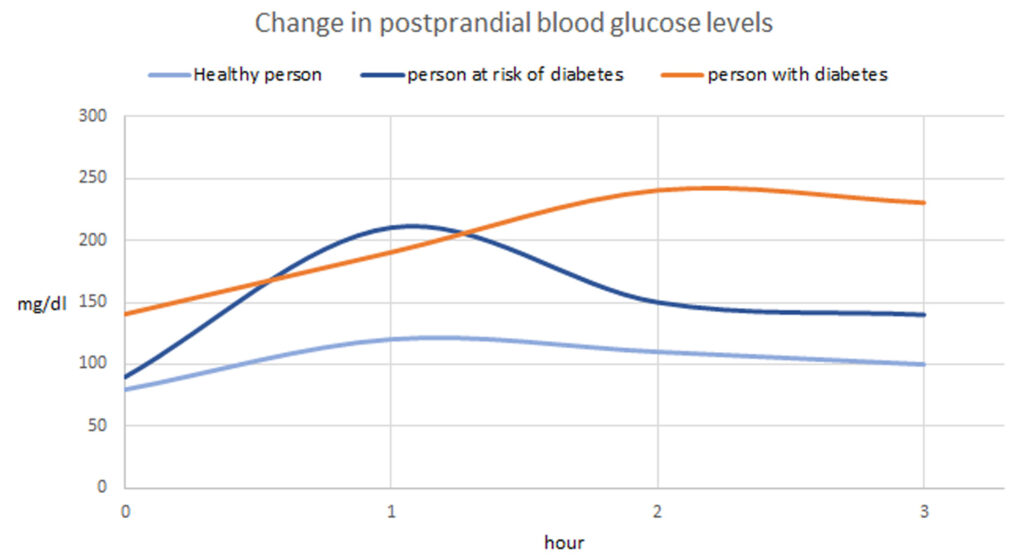
While healthy individuals experience a gentle rise and fall in post-meal blood sugar levels, those in the pre-diabetic category exhibit a sharp increase.This rapid rise and fall in post-meal blood sugar levels is referred to as a “blood sugar spike.” When blood sugar spikes occur, they can damage blood vessels, leading to arteriosclerosis and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Individuals with diabetes have persistently high blood sugar levels, and their levels do not decrease easily after meals. If high blood sugar levels persist, it can lead to what are known as the three major complications of diabetes: diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, and diabetic neuropathy.Additionally, metabolic syndrome refers to a high-risk health state characterized by visceral obesity, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and lipid metabolism disorders.
Below, we have compiled a table outlining the diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome and the judgment criteria for healthy individuals, pre-diabetic individuals, and individuals with diabetes.
Diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome
| Item | Criteria |
| Increased waist circumference | Men: 40 inches or more Women: 35 inches or more (measured around the entire abdomen) |
| High triglycerides | 150mg/dl or more |
| Low HDL-C | Men: less than 40mg/dL Women: less than 50mg/dL |
| Elevated blood pressure | Systolic blood pressure: 130mmHg or more and/or Diastolic blood pressure: 85mmHg or more |
| High fasting blood glucose | 100mg/dL or more |
If three out of the aforementioned five criteria are met, a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome is made.
Evaluation criteria for individuals who are healthy, at risk of diabetes, or already have diabetes
| Blood glucose levels two hours post-meal | Blood glucose levels during fasting | |
| Healthy person | 140 mg/dl or less | 110 mg/dl or less |
| Person with postprandial hyperglycemia | 140 to 200 mg/dl | 110 to 126 mg/dl |
| Person with diabetes | 200mg/dl or more | 126mg/dl or more |
Looking at the blood sugar levels, it becomes clear how people with metabolic syndrome, post-meal hyperglycemia, and diabetes differ from healthy individuals. In the case of being on the verge of diabetes, symptoms often do not manifest, so it’s important to be mindful of gently controlling blood sugar levels on a regular basis.
Why is Jerusalem Artichoke’s “Inulin” Beneficial in Reducing Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome Risks?
You may have heard that if you’re dealing with diabetes or metabolic syndrome, incorporating Jerusalem artichoke into your diet could be a game-changer. This is because Jerusalem artichoke is abundant in a nutrient known as “inulin,” which helps moderate the rise in blood sugar levels post meals.
Let’s delve into what Jerusalem artichoke is as a food item and explore effective ways to incorporate it into your diet.
What is Jerusalem Artichoke?
Jerusalem artichoke is a perennial plant belonging to the sunflower family. It’s a robust food source that thrives even in cold conditions and without the use of pesticides. It played a significant role during periods of food shortages during wartime.
Jerusalem artichoke is renowned for its high content of “inulin,” often referred to as natural insulin. Inulin has the ability to moderate post-meal blood sugar levels, making it an ideal choice for individuals dealing with diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Moreover, it contains a substantial amount of “potassium,” which inhibits the absorption of sodium in the body and aids urination. This is said to be effective in preventing high blood pressure. Another attractive feature is its lower starch content compared to other tubers, resulting in fewer carbohydrates and calories.
Inulin’s Role in Moderating Post-Meal Blood Sugar Levels
Among the various nutrients found in Jerusalem artichoke, let’s focus on “inulin,” which aids in reducing the risk of diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Inulin is a water-soluble dietary fiber that dissolves readily in water. It is expected to gently regulate sugar absorption, thereby moderating the rise in blood sugar levels.
Studies conducted by clinical trial institutions have corroborated these effects. They examined the progression of post-meal blood sugar levels in individuals who consumed supplements with inulin and those who consumed supplements without inulin. The findings revealed that individuals who ingested inulin experienced a more gradual increase in post-meal blood sugar levels.
| Before Consumption | 30 minutes Later | 60 minutes Later | 120 minutes Later | |
| Individuals who have consumed a supplement containing inulin | 94.1±7.9 | 121.2±9.5 | 112.6±8.1 | 92.1±4.1 |
| Individuals who have consumed a supplement that does not contain inulin | 93.6±3.6 | 148.1±9.2 | 126.6±10.8 | 96.3±7.1 |
Data collected 12 weeks after the start of the trial.
Effective Consumption of Jerusalem Artichoke
To effectively ingest inulin, it’s important to consider how you consume it. Jerusalem artichoke begins to lose its inulin content after harvest, so it’s recommended to consume it as fresh as possible if eating it raw. However, consistently purchasing fresh produce and preparing it immediately can be challenging.
If you’re looking for a convenient way to incorporate inulin into your daily diet, supplements are a great option. They eliminate the need for preparation and can be consumed whenever convenient. If you’re concerned about diabetes or metabolic syndrome, consider checking out the product details on platforms like Amazon.
Wrapping Up
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the advantages of incorporating Jerusalem artichoke into your diet, the most effective ways to consume it, and the optimal changes in blood sugar levels for individuals managing diabetes or metabolic syndrome. Jerusalem artichoke, rich in “inulin” – often dubbed as natural insulin, is considered beneficial for those dealing with diabetes or metabolic syndrome. However, to maximize the benefits of inulin, it’s ideal to consume Jerusalem artichoke as fresh as possible. Given this, utilizing supplements can offer a practical and hassle-free approach to maintaining your health. Consider making them a part of your daily wellness routine.

